PASSAGE 1 Renewable Energy
An insight into the progress in renewable energy research
A
The race is on for the ultimate goal of renewable energy: electricity production at prices that are competitive with coal-fired power stations, but without coal’s pollution. Some new technologies are aiming to be the first to push coal from its position as Australia’s chief source of electricity.
B
At the moment the front-runner in renewable energy is wind technology. According to Peter Bergin of Australian Hydro, one of Australia’s leading wind energy companies, there have been no dramatic changes in windmill design for many years, but the cumulative effects of numerous small improvements have had a major impact on cost. ‘We’re reaping the benefits of 30 years of research in Europe, without have to make the same mistakes that they did,’ Mr Bergin says.
C
Electricity can be produced from coal at around 4 cents per kilowatt-hour, but only if the environmental costs are ignored. ‘Australia has the second cheapest electricity in the world, and this makes it difficult for renewable to compete,’ says Richard Hunter of the Australian Ecogeneration Association (AEA). Nevertheless, the AEA reports: ‘The production cost of a kilowatt-hour of wind power is one-fifth of what it was 20 years ago,’ or around 7 cents per kilowatt-hour.
D
Australian Hydro has dozens of wind monitoring stations across Australia as part of its aim to become Australia’s pre-eminent renewable energy company. Despite all these developments, wind power remains one of the few forms of alternative energy where Australia is nowhere near the global cutting edge, mostly just replicating European designs.
E
While wind may currently lead the way, some consider a number of technologies under development have more potential. In several cases, Australia is at the forefront of global research in the area. Some of them are very site- specific, ensuring that they may never become dominant market players. On the other hand, these newer developments are capable of providing more reliable power, avoiding the major criticism of windmills – the need for back-up on a calm day.
F
One such development uses hot, dry rocks. Deep beneath South Australia, radiation from elements contained in granite heats the rocks. Layers of insulating sedimentation raise the temperatures in some location to 250° centigrade. An Australian firm, Geoenergy, is proposing to pump water 3.5 kilometres into the earth, where it will travel through tiny fissures in the granite, heating up as it goes until it escapes as steam through another
G
No greenhouse gases are produced, but the system needs some additional features if it is to be environmentally friendly. Dr Prue Chopra, a geophysicist at the Australian National University and one of the founders of Geoenergy, note that the steam will bring with it radon gas, along through a heat exchanger and then sent back underground for another cycle. Technically speaking, hot dry rocks are not a renewable source of energy. However, the Australian source is so large it could supply the entire country’s needs for thousands of years at current rates of consumption.
H
Two other proposals for very different ways to harness sun and wind energy have surfaced recently. Progress continues with Australian company EnviroPower’s plans for Australia’s first solar chimney near Mildura, in Victoria. Under this scheme, a tall tower will draw hot air from a greenhouse built to cover the surrounding 5 km2. As the air rises, it will drive a turbine* to produce electricity. The solar tower combines three very old technologies – the chimney, the turbine and the greenhouse – to produce something quite new. It is this reliance on proven engineering principles that led Enviropower’s CEO, Richard Davies, to state: There is no doubt this technology will work, none at all.’
I
This year, Enviropower recognized that the quality of sunlight in the Mildura district will require a substantially larger collecting area than was previously thought. However, spokesperson kay Firth says that a new location closer to Mildura will enable Enviropower to balance the increased costs with extra revenue. Besides saving in transmission costs, the new site ‘will mean increased revenue from tourism and use of power for telecommunications. We’ll also be able to use the outer 500 metres for agribusiness.’ Wind speeds closer to the tower will be too high for farming.
J
Another Australian company, Wavetech, is achieving success with ways of harvesting the energy in waves. Wavetech’s invention uses a curved surface to push waves into a chamber, where the flowing water column pushes air back and forth through a turbine. Wavetech was created when Dr Tim Devine offered the idea to the world leader in wave generator manufacturers, who rather surprisingly rejected it. Dr Devine responded by establishing Wavetech and making a number of other improvements to generator design. Wavetech claims that, at appropriate sites, ‘the cost of electricity produced with our technology should be below 4 cents per kilowatt- hour.
K
The diversity of forms of greenhouse – friendly energy under development in Australia is remarkable. However, support on a national level is disappointing. According to Richard Hunter of the AEA, ‘Australia has huge potential for wind, sun and wave technology. We should really be at the forefront, but the reality is we are a long way behind.’
Questions 1-7
Do the following statements agree with the information given in Reading Passage?
In boxes 1-7 on your answer sheet, write
TRUE if the statement agrees with the information
FALSE if the statement contradicts the information
NOT GIVEN if there is no information on this
1/ In Australia, alternative energies are less expensive than conventional electricity.
2/ Geoenergy needs to adapt its system to make it less harmful to the environment.
3/ Dr Prue Chopra has studied the effects of radon gas on the environment.
4/ Hot, dry rocks could provide enough power for the whole of Australia.
5/ The new Enviropower facility will keep tourists away.
6/ Wavetech was established when its founders were turned down by another company.
7/ According to AEA, Australia is a world leader in developing renewable energy.
Questions 8-13
Look at the following statements (Questions 8-13) and the list of companies below.
Match each statement with the correct company, A-D.
Write the correct letter, A-D, in boxes 8-13 on your answer sheet.
NB You may use any letter more than once.
8/ During the process, harmful substances are prevented from escaping.
9/ Water is used to force air through a special device.
10/ Techniques used by other countries are being copied.
11/ The system can provide services other than energy production
12/ It is planned to force water deep under the ground.
13/ Original estimates for part of the project have been revised.
List of Companies
A Australian Hydro
B Geoenergy
C Enviropower
D Wavetech
PASSAGE 2: The Impact of Environment to Children
A
What determines how a child develops? In reality, it would be impossible to account for each and every influence that ultimately determines who a child becomes. What we can look at are some of the most apparent influences such as genetics, parenting, experiences, friends, family relationships and school to help us understand the influences that help contribute to a child’s growth.
B
Think of these influences as building blocks. While roost people tend to have the same basic building blocks, these components can be put together in an infinite number of ways. Consider your own overall personality. How much of who you are today was shaped by your genetic inheritance, and how much is a result of your lifetime of experiences? This question has puzzled philosophers, psychologists and educators for hundreds of years and is frequently referred to as the nature versus nurture debate. Generally, the given rate of influence on children is 40 % to 50%. It may refer to all of siblings of a family. Are we the result of nature (our genetic background) or nurture (our environment)? Today, most researchers agree that child development involves a complex interaction of both nature and nurture, while some aspects of development may be strongly influenced by biology, environmental influences may also play a role. For example, the timing of when the onset of puberty occurs is largely the results of heredity, but environmental factors such as nutrition can also have an effect.
C
The From the earliest moments of life, the interaction of heredity and the environment works to shape who children are and who they will become. While the genetic instructions a child inherits from his parents may set out a road map for development, the environment can impact how these directions are expressed, shaped or event silenced. The complex interaction of nature and nurture does not just occur at certain moments or at certain periods of time; it is persistent and lifelong.
D
The shared environment (also called common environment) refers to environmental influences that have the effect of making siblings more similar to one another. Shared environmental influences can include shared family experiences, shared peer groups, and sharing the same school and community. In general, there has not been strong evidence for shared environmental effects on many behaviors, particularly those measured in adults. Possible reasons for this are discussed. Shared environmental effects are evident in children and adolescents, but these effects generally decrease across the life span. New developments in behavior genetic methods have made it possible to specify shared environments of importance and to tease apart familial and nonfamilial sources of shared environmental influence. It may also refer to all of siblings of a family, but the rate of influence is less than 10 per cent.
E
The importance of non-shared environment lay hidden within quantitative genetic studies since they began nearly a century ago. Quantitative genetic methods, such as twin and adoption methods, were designed to tease apart nature and nurture in order to explain family resemblance. For nearly all complex phenotypes, it has emerged that the answer to the question of the origins of family resemblance is nature-things run in families primarily for genetic reasons. However, the best available evidence for the importance of environmental influence comes from this same quantitative genetic research because genetic influence never explains all of the variances for complex phenotypes, and the remaining variance must be ascribed to environmental influences. Non-shared environment, it may refer to the part of siblings of a family, the rate of influence to children is 40 % to 50%.
F
Yet it took many decades for the full meaning of these findings to emerge. If genetics explains why siblings growing up in the same family are similar, but the environment is important, then it must be the case that the salient environmental effects do not make siblings similar. That is, they are not shared by children growing up in the same family-they must be ‘non-shared’. This implication about non-shared environmental import lay fallow in the field of quantitative genetics because the field’s attention was then firmly on the nature-nurture debate. ‘Nurture’ in the nature-nurture debate was implicitly taken to mean shared environment because, from Freud onwards, theories of socialization had assumed that children’s environments are doled out on a family-by-family basis. In contrast, the point of the non-shared environment is that environments are doled out on a child-by-child basis. Note that the phrase ‘non-shared environment’ is shorthand for a component of phenotypic variance-it refers to ‘effects’ rather than ‘events’, as discussed later. Research in recent years suggested that the impact from parents will be easy to be interrupted by the influence from the children of the same age. That also showed that variations of knowledge that children get from other culture are increasing. A number of interests between, whatever, fathers and mothers or parents and their children are conflicting.
G
Because siblings living in the same home share some but not all of the potential genetic and environmental factors that influence their behaviors, teasing apart the potential influences of genetic and non-genetic factors that differentiate siblings is very difficult. Turkheimer and Waldron (2000) have noted that non-shared environmental influences——which include all of the random measurement error——may not be systematic, but instead may operate idiosyncratically and in ways that cannot be ascertained. Thus, the question is whether or not quasi-experimental behavioral genetic designs can be used to actually identify systematic non-shared environmental mechanisms cross-sectionally and longitudinally. This is the impetus for the current study.
Questions 1-5 Complete the table now. Choose NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS from the Reading Passage for each answer.

Questions 6-8 Complete the following summary of the paragraphs of Reading Passage. Using NO MORE THAN
THREE WORDS from the Reading Passage for each answer. Write your answers in boxes 6-8 on your answer sheet.
Research in recent years illuminated that the impact from parents will frequently be 6…………………. by the peer’s pressure. It was also indicated that 7………………… of knowledge that children learned from other culture is increasing. The study has found quantities of competing 8………………… between parents and children or even between parents themselves.
Questions 9-12 Do the following statements agree with the claims of the writer in Reading Passage
In boxes 9-12 on your answer sheet, write
YES if the statement agrees with the claims of the writer
NO if the statement contradicts the claims of the writer
NOT GIVEN if it is impossible to say what the writer thinks about this
9………………… The more children there are in a family, the more impacts of environment it is.
10………………… Methods based on twin studies still meet unexpected differences that cannot be ascribed to be
a purely genetic explanation.
11………………… Children prefer to speak the language from the children of the same age to the language
spoken by their parents.
12………………… The Study of non-shared environment influence can be a generally agreed idea among researchers in the field.
Question 13 Choose the correct letter, A, B, C, or D.
Write your answers in box 13 on your answer sheet
According to this passage, which comment is TURE about the current Study of non-shared environment influence to children?
A a little biased in nature
B not sufficiently proved
C very systematic
D can be workable
PASSAGE 3: What Are Dreams ?
A
Thousands of years ago, dreams were seen as messages from the gods, and in many cultures, they are still considered prophetic. In ancient Greece, sick people slept at the temples of Asclepius, the god of medicine, in order to receive dreams that would heal them. Modern dream science really begins at the end of the 19th century with Sigmund Feud, who theorized that dreams were the expression of unconscious desires often stemming from childhood. He believed that exploring these hidden emotions through analysis could help cure mental illness. The Freudian model of psychoanalysis dominated until the 1970s when new research into the chemistry of the brain showed that emotional problems could have biological or chemical roots, as well as environmental ones. In other words, we weren’t sick just because of something our mothers did (or didn’t do), but because of some imbalance that might be cured with medication.
B
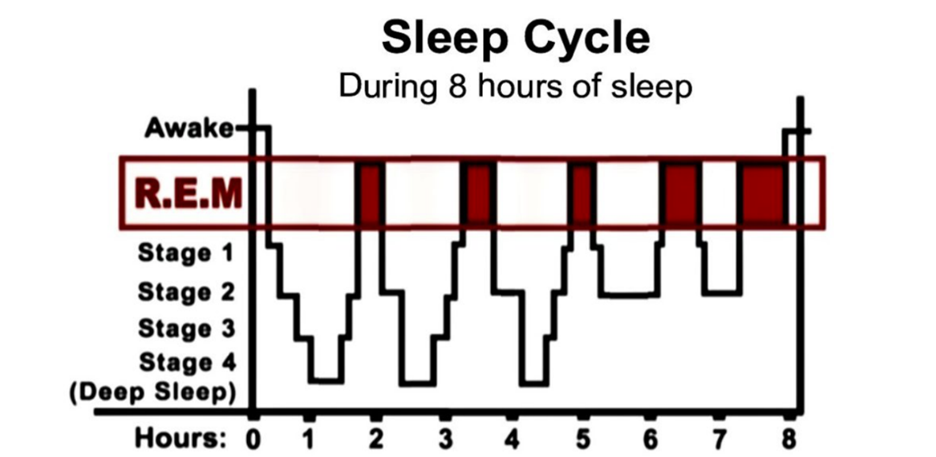
After Freud, the most important event in dream science was the discovery in the early 1950s of a phase of sleep characterized by intense brain activity and rapid eye movement (REM). People awakened in the midst of REM sleep reported vivid dreams, which led researchers to conclude that most dreaming took place during REM. Using the electroencephalograph (EEG), researchers could see that brain activity during REM resembled that of the waking brain. That old them that a lot more was going on at night than anyone had suspected. But what, exactly?
C
Scientists still don’t know for sure, although they have lots of theories. On one side are scientists like Harvard’s Allan Hobson, who believes that dreams are essentially random. In the 1970s, Hobson and his colleague Robert McCarley proposed what they called the “activation-synthesis hypothesis’” which describes how dreams are formed by nerve signals sent out during REM sleep from a small area at the base of the brain called the pons. These signals, the researchers said, activate the images that we call dreams. That put a crimp in dream research; if dreams were meaningless nocturnal firings, what was the point of studying them?
D
Adult humans spend about a quarter of their sleep time in REM, much of it dreaming. During that time, the body is essentially paralyzed but the brain is buzzing. Scientists using PET and fMRI technology to watch the dreaming brain have found that one of the most active areas during REM is the limbic system, which controls our emotions. Much less active is the prefrontal cortex, which is associated with logical thinking. That could explain why dreams in REM sleep often lack a coherent storyline (some researchers have also found that people dream in non-REM sleep as well, although those dreams generally are less vivid.) Another active part of the brain in REM sleep is the anterior cingulate cortex, which detects discrepancies. Eric Nofzinger, director of the Sleep Neuroimaging Program at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, thinks that could be why people often figure out thorny problems in their dreams. “As if the brain surveys the internal milieu and tries to figure out what it should be doing, and whether our actions conflict with who we are,” he says.
E
These may seem like vital mental functions, but no one has yet been able to say that REM sleep or dreaming is essential to life or even sanity. MAO inhibitors, an older class of antidepressants, essentially block REM sleep without any detectable effects, although people do get a “REM rebound” – extra REM – if they stop the medication. That’s also true of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like Prozac, which reduce dreaming by a third to a half. Even permanently losing the ability to dream doesn’t have to be disabling. Israeli researcher Peretz Lavie has been observing a patient named Yuval Chamtzani, who was injured by a fragment of shrapnel that penetrated his brain when he was 19. As a result, he gets no REM sleep and doesn’t remember any dreams. But Lavie says that Chamtzani, now 55, “is probably the most normal person I know and one of the most successful ones.” He’s a lawyer, a painter and the editor of a puzzle column in a popular Israeli newspaper.
F
The mystery of REM sleep is that even though it may not be essential, it is ubiquitous – at least in mammals and birds. But that doesn’t mean all mammals and birds dream (or if they do, they’re certainly not – talking about it). Some researchers think REM may have evolved for physiological reasons. “One thing that’s unique about mammals and birds is that they regulate body temperature”, says neuroscientist Jerry Siegel, director of UCLA’s Center for Sleep Research. “There’s no good evidence that any coldblooded animal has REM sleep.” REM sleep heats up the brain and non-REM cools it off, Siegel says, and that could mean that the changing sleep cycles allow the brain to repair itself. “It seems likely that REM sleep is filling a basic physiological function and that dreams are a kind of epiphenomenon,” Siegel says – an extraneous byproduct; like foam on beer.
G
Whatever the function of dreams at night, they clearly can play a role in therapy during the day. The University of Maryland’s Clara Hill, who has studied the use of dreams in therapy, says that dreams are a ‘backdoor’, into a patient’s thinking. “Dreams reveal stuff about you that you didn’t know was there,” she says. The therapists she trains to work with patients’ dreams are, in essence, heirs to Freud, using dream imagery to uncover hidden emotions and feelings. Dreams provide clues to the nature of the more serious mental illness. Schizophrenics, for example, have poor-quality dreams, usually about objects rather than people. “If you’re going to understand human behavior,” says Rosalind Cartwright, a chairman of psychology at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, “here’s a big piece of it. Dreaming is our own storytelling time – to help us know who we are, where we’re going and how we’re going to get there.” Cartwright has been studying depression in divorced men and women, and she is finding that “good dreamers,” people who have vivid dreams with strong storylines, are less likely to remain depressed. She thinks that dreaming helps diffuse strong emotions. “Dreaming is a mental-health activity,” she says.
Questions 1-5
Reading Passage has seven paragraphs, A-G.
Which paragraph contains the following information?
Write the correct number, A-G, in boxes 1-5 on your answer sheet.
1/ Reference of an artist’s dreams who has versatile talents
2/ The dream actually happens to many animals
3/ Dreams are related to benefit and happiness
4/ advanced scientific technology applied in the investigation of the REM stage.
5/ questioning concern raised about the usefulness of investigation on dreams
Questions 6-8
Choose the correct letter, A, B, C or D.
Write your answers in boxes 6-8 on your answer sheet.
6/ What were dreams regarded as by ancient people?
A superstitious and unreliable
B communication with gods and chance to predict the future
C medical relief for children with an ill desire
D rules to follow as they fell asleep in a temple
7/ According to Paragraph D, which part of the brain controls reasoning?
A anterior cingulate cortex
B internal cortex
C limbic system
D prefrontal cortex
8/ What can we conclude when the author cited a reference for dreams in animals?
A Brain temperature rises when REM pattern happens.
B The reason why mammals are warm-blooded
C mammals are bound to appear with more frequent REM.
D REM makes people want to drink beer with more foam.
Questions 9-14
Look at the following people and the list of statements below.
Match each statement with the correct person, A-G.
Write the correct letter, A-G, in boxes 9-14 on your answer sheet.
List of people
A Sigmund Freud
B Allan Hobson (Harvard)
C Robert McCarley
D Eric Nofzinger
E Jerry Siegel
F Clara Hill
G Rosalind Cartwright
9/ Dreams sometimes come along with REM as no more than a trivial attachment
10/ Exploring patients’ dreams would be beneficial for treatment as it reveals the unconscious thinking
11/ Dreams help people cope with the difficulties they meet in the daytime
12/ Decoding dreams would provide a reminder to human desire in the early days
13/ Dreams are a body function to control strong emotion
14 Dreams seem to be as randomly occurring and have limited research significance.